El Niño And La Niña: Influences On Hurricane Activity
El Niño and La Niña: Influences on Hurricane Activity
Introduction
Hurricanes are one of the most destructive natural disasters that can affect coastal areas. They can bring about devastating winds, storm surges, flooding, and heavy rains that lead to loss of life, destruction of property, and disruption of economic activities. In recent years, there has been increased concern about the impact of climate change on hurricane activity, and scientists have been studying the relationship between El Niño and La Niña and their effects on hurricanes.
The Basics of El Niño and La Niña
What are El Niño and La Niña?
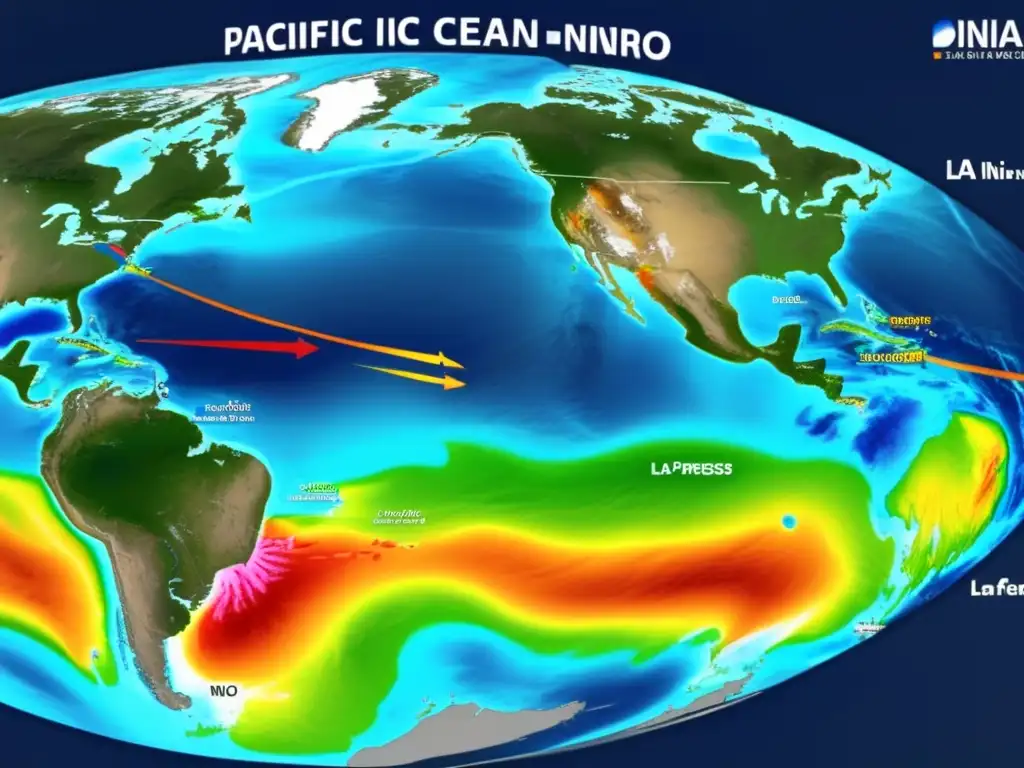
El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of a natural climate pattern called the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO). ENSO is characterized by changes in sea surface temperatures, air pressure, and winds in the tropical Pacific Ocean. During El Niño, warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures occur in the eastern Pacific Ocean, while during La Niña, cooler-than-usual sea surface temperatures occur in the same region.
How do El Niño and La Niña affect global weather patterns?
El Niño and La Niña can significantly influence weather patterns around the world by changing atmospheric circulation patterns. During El Niño, there is a weakening of Walker Circulation, which results in warmer and drier conditions in some regions (e.g., Australia, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa) and cooler and wetter conditions in others (e.g., southern South America and the southern United States). During La Niña, there is a strengthening of Walker Circulation, which leads to cooler and wetter conditions in some regions (e.g., western Canada and the Pacific Northwest) and warmer and drier conditions in others (e.g., the southern United States and southeastern Brazil).
How often do El Niño and La Niña occur?
El Niño and La Niña events occur irregularly, but on average, there is an El Niño or La Niña event every two to seven years. Historically, El Niño events have been more common than La Niña events.
The Relationship Between El Niño/La Niña and Hurricane Activity

What is the relationship between El Niño/La Niña and hurricane activity?
There is a well-established link between El Niño/La Niña and hurricane activity. During an El Niño event, the Atlantic Ocean tends to experience higher wind shear, which can suppress the formation and intensification of tropical cyclones. In contrast, during a La Niña event, the Atlantic Ocean experiences lower wind shear, which can enhance the formation and intensification of tropical cyclones. This is because wind shear creates an unfavorable environment for tropical cyclones to form and develop by disrupting their organization and reducing their ability to take in moisture and energy from the ocean.
Does ENSO affect other basins besides the Atlantic basin?
Yes. El Niño and La Niña can also significantly impact hurricane activity in other basins, including the eastern Pacific Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean. During El Niño, there tends to be an increase in tropical cyclone activity in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean, while the western Pacific Ocean experiences fewer storms. During La Niña, the opposite occurs, with an increase in storms in the western Pacific Ocean and a decrease in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean.
The Implications of El Niño/La Niña on Hurricane Preparedness

What are the implications of El Niño/La Niña on hurricane preparedness?
El Niño/La Niña can have significant implications for hurricane preparedness. If there is an El Niño event, it is recommended that coastal residents prepare for a quieter hurricane season with fewer storms. However, residents should still remain vigilant and take necessary precautions when a storm does occur. In contrast, if there is a La Niña event, it is recommended that coastal residents be extra vigilant and make necessary preparations for a potentially more active hurricane season.
How do El Niño/La Niña affect hurricane forecasting?
El Niño/La Niña events can also impact hurricane forecasting by influencing the track and intensity of storms. For example, during an El Niño event, there tends to be an increased possibility of storms tracking further to the east, which can increase the likelihood of a hurricane making landfall in the Gulf Coast region. On the other hand, during a La Niña event, there tends to be an increased possibility of storms tracking closer to the U.S. East Coast.
Frequently Asked Questions

-
Can El Niño or La Niña cause a hurricane on its own?
No. El Niño/La Niña do not cause hurricanes, but they can influence the formation and intensification of storms by creating favorable or unfavorable atmospheric and oceanic conditions.
-
What is the difference between a tropical storm and a hurricane?
A tropical storm has maximum sustained winds of 39-73 mph, while a hurricane has maximum sustained winds of 74 mph or higher.
-
How can I prepare for a hurricane?
You can prepare for a hurricane by creating an emergency kit, developing an evacuation plan, securing your home, and staying informed about the latest weather developments.
-
What should I do during a hurricane?
You should stay indoors, away from windows and doors, and follow all advice and instructions from local authorities. If you are ordered to evacuate, do so immediately.
-
What should I do after a hurricane?
You should stay safe and avoid hazards, assess the damage to your property and belongings, contact your insurance company, and apply for assistance if necessary.
Conclusion
El Niño/La Niña have significant implications for hurricane activity, which can impact coastal residents and communities. Understanding the relationship between El Niño/La Niña and hurricane activity is crucial for preparedness, forecasting, and response efforts. By staying informed and taking necessary precautions, coastal residents and communities can minimize the risks associated with hurricanes and protect themselves and their property.
If you live in a hurricane-prone area, it is recommended that you stay up to date with the latest weather developments and follow all advice and instructions from local authorities. Additionally, it is important to have an emergency plan in place and to prepare an emergency kit with essential supplies. Your preparation and vigilance can make a significant difference in keeping yourself and those around you safe.
Additional Resources
 Cyclones, Typhoons, And Hurricanes: Different Names, Same Phenomena
Cyclones, Typhoons, And Hurricanes: Different Names, Same Phenomena The History And Development Of Hurricane Forecasting
The History And Development Of Hurricane Forecasting The Relationship Between Ocean Temperatures And Hurricanes
The Relationship Between Ocean Temperatures And HurricanesIf you want to discover more articles similar to El Niño And La Niña: Influences On Hurricane Activity, you can visit the Basic knowledge about hurricanes: category.
Leave a Reply

Articulos relacionados: