The Long-term Environmental Effects Of Hurricanes

The Long-term Environmental Effects of Hurricanes
Introduction
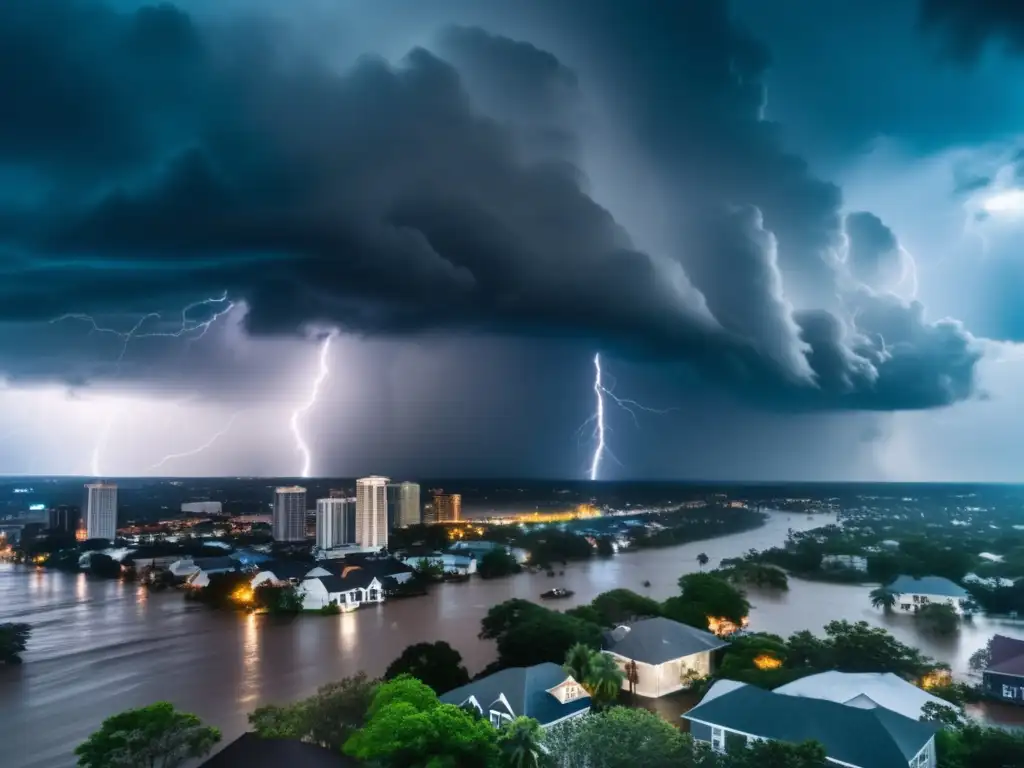
As natural calamities, hurricanes can have devastating effects not only on the human population but also on the environment. Beyond the immediate destruction caused by these storms, hurricanes have long-term environmental impacts that are often overlooked. In this article, we will explore the various ways hurricanes affect the environment in the long term.
Soil Erosion and Nutrient Depletion

Coastal Regions
In coastal regions, hurricanes can cause significant soil erosion and nutrient depletion, mainly due to storm surges, which move sand and sediment towards the shore. This process reduces the amount of fertile soil available for plant growth, leading to reduced agricultural productivity. Additionally, the influx of saltwater can damage plant roots and disrupt the balance of nutrients in the soil, making it more challenging for vegetation to grow and thrive in the future.
Inland Regions
Hurricanes can also have long-term effects on inland regions. Heavy rainfall associated with hurricanes can lead to severe flooding, which can wash away soil and diminish its nutrient content. This process can be exacerbated in areas where deforestation or other forms of land degradation have taken place, as there is less vegetation to hold soil in place. Over time, this can lead to a reduction in soil fertility, making it challenging for plants to grow and thrive.
Ocean
In addition to soil erosion and nutrient depletion, hurricanes can also have long-term effects on the ocean ecosystem. Storm surges can disturb the seafloor, leading to the release of sediment and nutrients into the water. This process can create algal blooms, which can consume excessive amounts of oxygen in the water, leading to "dead zones" that suffocate fish and other marine life. Moreover, hurricanes can cause the death of coral reefs, a critical marine ecosystem, by damaging it with strong waves and winds, leading to long-term effects on the marine biodiversity that rely on these reefs.
Climate Change

Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Hurricanes can also contribute to climate change by releasing large quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide emitted from decaying organic matter from vegetation destroyed by hurricanes is one such example. Additionally, wildfires that are triggered by lightning strikes from the storm can contribute to carbon emissions, further exacerbating the effects of climate change in other regions.
Rising Sea Levels
Another long-term environmental impact of hurricanes is the potential rise in sea levels as a result of the melting of glaciers and ice sheets due to global warming. Hurricanes can add to this rise by increasing the amount of water deposited on land, which ultimately ends up back in the ocean, contributing to the overall sea level rise. The resulting increase in sea level and storm surges heightens the risk of coastal flooding, which can have severe consequences for both people and wildlife living in these areas.
Biodiversity Loss

Animal Populations
Finally, hurricanes can also lead to long-term losses of biodiversity. Animal populations, including both large and small animals, can experience significant losses due to extreme weather events. This loss can have ripple effects throughout entire ecosystems, including alterations to food webs and population dynamics. For example, hurricanes can destroy habitats or displace animals, leading to a decline in their population. This can, in turn, affect the populations of other species that rely on each other in the ecosystem.
Plant Species
In addition to animal populations, hurricanes can also lead to the loss of plant species, particularly in areas where storms lead to the widespread destruction of forests and other natural habitats. Trees that may have taken decades or even centuries to grow can be easily destroyed by hurricane-force winds. This results in a significant loss of foliage and habitat for wildlife, which can have long-term impacts on the ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions

-
Do hurricanes contribute to climate change?
Yes, hurricanes can contribute to climate change by releasing large quantities of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide from decaying vegetation and wildfires triggered by lightning strikes from the storm.
-
How do hurricanes affect soil erosion?
Hurricanes cause soil erosion by moving sediment and sand towards the shore, reducing the amount of fertile soil available for plant growth. This can lead to reduced agricultural productivity in coastal regions.
-
How do hurricanes affect marine ecosystems?
Hurricanes can cause damage to coral reefs, create algal blooms and "dead zones" that suffocate fish and other marine life by consuming excessive oxygen in the water, and disturb the seafloor.
-
Can hurricanes lead to a loss of biodiversity?
Yes, hurricanes can lead to a loss of biodiversity by destroying habitats and displacing animal populations.
-
What are the long-term effects of hurricanes on the environment?
The long-term effects of hurricanes on the environment include soil erosion and nutrient depletion, climate change, and biodiversity loss.
Conclusion
Hurricanes have a significant impact on the environment, not only in the immediate aftermath but also in the long term. Soil erosion and nutrient depletion, climate change, and biodiversity loss are just some of the ways that hurricanes can affect the environment. As we continue to witness increasingly more severe hurricanes due to climate change, understanding the long-term effects of these storms is essential. By taking steps to mitigate the damage caused by hurricanes, we can work towards a more sustainable future for our planet.
Additional Resources

- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) – Hurricane Impacts on Ecosystems, available online at: [https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/hurricane-ecosystems.html]
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR) - The Impact of Hurricanes on Biodiversity, available online at: [https://www.undrr.org/news/impact-hurricanes-biodiversity]
- National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) – Effects of Climate Change, available online at: [https://climate.nasa.gov/effects/]
 Hurricanes In Pop Culture: Movies And Documentaries
Hurricanes In Pop Culture: Movies And Documentaries The Day After: What Happens To A Community After A Hurricane?
The Day After: What Happens To A Community After A Hurricane? The Most Active Hurricane Seasons On Record
The Most Active Hurricane Seasons On RecordIf you want to discover more articles similar to The Long-term Environmental Effects Of Hurricanes, you can visit the Basic knowledge about hurricanes: category.
Leave a Reply

Articulos relacionados: